What is a database and it’s types ?
To understand “what MySQL is”, we first need to explore what databases are, how they work, and why they are used. Let’s begin by understanding the concept of databases. Think of a database like an almirah (cabinet) where you neatly organize different types of books. This makes it easy to find exactly what you need, whenever you need it.
Similarly, when a website handles large amounts of data—like user information, orders, or content—we need a place to store and organize that data efficiently. That’s where a “database” comes in.
A database helps store all types of information in one place and allows us to retrieve it quickly whenever required.
Databases are generally of two types: relational databases and non-relational databases.
Relational databases store data in a tabular format, where data is organized into rows and columns. Each column has its own specific data type.
The data in one table can be related to data in another table using a referential key, commonly known as a foreign key.
This relationship allows structured and organized storage, retrieval, and manipulation of data. MySQL is a popular example of a relational database management system (RDBMS) that uses this tabular structure to store and manage data efficiently.
Non-relational databases are a bit different from relational databases. In a non-relational database, the data is not organized in tables.
Instead, non-relational databases handle unstructured or semi-structured data. They offer a more flexible way of storing data compared to relational databases.
These databases follow different data models such as key-value pairs, documents, graphs, and more. Best example of non-relational databases are MongoDB, Redis, etc .
MySQL is the most popular relational database. It stores data in a table format using rows and columns. Each row uniquely identifies a record.
This record can be linked to a row in another table using a referential key, known as a foreign key. The key that uniquely identifies a row is called the primary key.
MySQL is open-source and can be downloaded and used free of cost. It also has a large community that provides support.
MySQL uses SQL commands to fetch, insert, update, and delete records. It is capable of storing huge and complex datasets and handling high-volume traffic.
MySql is a cross-platform .It can run on multiple operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Why and where we use MySql ?
In dynamic websites we take various user inputs like their personal information, orders, comments ,wishlist ,enquiries. Store owners need all these data to be stored at one place to process further for their transactions and communication.So we need a database for this.So store owners use MySql as a database to store all the information as it’s free and easy to use. CMS like WordPress,OsCommerce,Opencart which are opensource solutions for ecommerce uses MySql as a database.MySql can also be used with custom web applications powered by frameworks like Codeigniter and Laravel.
How does MySql database interacts with a Web Application ?
To understand how a web application uses Mysql lets see the below diagram
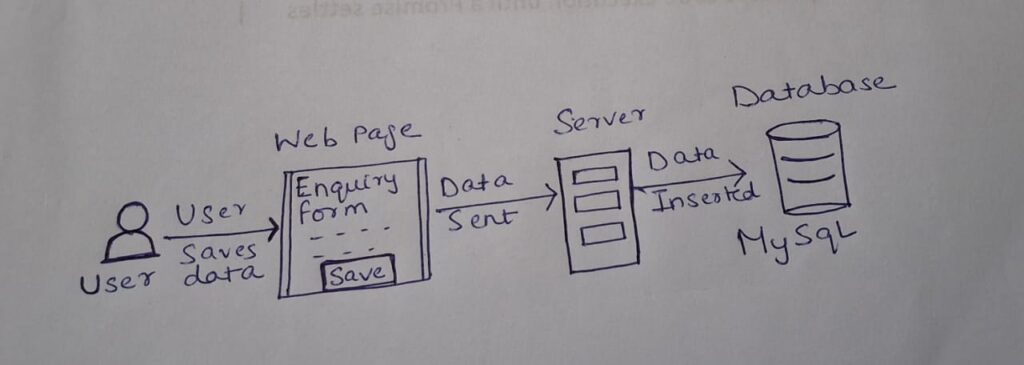
In this diagram, we can see an enquiry form on a webpage. A user enters all the required information and clicks the “Save” button.
When the form is submitted, the data is sent to the server. On the server side, the code attempts to connect to the MySQL database using the database username, password, and hostname.
Once the connection is successful, the data can be saved into the appropriate table in the database using an SQL command like INSERT.
Understanding databases is crucial for anyone starting in web development, and MySQL is one of the most widely used relational database systems today. It provides a structured, reliable, and scalable way to store and manage data, making it an essential tool for dynamic websites and applications. Whether you’re working with WordPress, building an eCommerce store, or developing a custom web app, knowing how MySQL works will give you a solid foundation.
As you move forward, exploring MySQL commands, queries, and real-world use cases will help you become more confident in handling databases in your projects.
